This module provides a brief introduction to the topic of nature-based solutions for holiday home development.
Objectives
Establish a common language about nature-based solutions (NBL) and ecosystem services.
Understand why NBL is relevant to the holiday home field (plot → field → landscape).
Clarify the level of ambition (avoid–limit–restore/enhance) and success criteria.
Prepare the project for a decision-making process with clear "gates" (go/adjust/no).
What is NBL?
Measures that use nature's own processes (vegetation, soil, water, topography, microclimate) to solve challenges such as stormwater, erosion, heat, biodiversity and well-being - while reducing environmental impacts and operating costs.
Why NBL in holiday home development?
Robustness and risk : Open waterways, diversions and native plants reduce flooding/erosion.
Cost/benefit : Less blasting/masses, lower technical complexity → lower CAPEX/OPEX.
Quality and acceptance : Site adaptation provides better landscape adaptation, well-being and local legitimacy.
Nature and climate values : Carbon sequestration, pollinators, cooling effect, increased biodiversity.
NBL is not "decoration" at the end of a project. It is the guiding premise for location, design and implementation – from site selection to operation and maintenance.
-
Ecosystem services are the benefits that nature provides us – either directly, such as food and clean water, or indirectly, such as pollination, flood mitigation and aesthetic qualities.
In planning and design, it is crucial to highlight how an area already provides such services, and how new measures can either strengthen or weaken them.
Ecosystem services are the functions and benefits that nature provides us – directly or indirectly – and which are fundamental to both human welfare and societal development.
-
Nature-based solutions (NBS) aim to solve societal challenges by taking natural processes and ecosystems as a starting point. These can be social, economic or environmental challenges, such as climate change, pollution or loss of nature.
Nature-based solutions can be purely natural measures such as nature conservation or restoration, or they can be used in combination with more technical, engineered measures, such as rain beds with natural aquatic plants that mimic natural processes and ecosystems.
Nature-based solutions also provide a number of other positive effects, such as sequestering carbon, improving air quality, providing opportunities for recreation and social gatherings. Nature-based solutions should be developed through inclusive processes with residents.
Good examples
Hovinbekken, Oslo – reopened waterway as a premise
What does the case show?
Open, nature-based stormwater solutions (stream opening, diversion in green areas) that simultaneously provide flood mitigation, a cooling effect, natural diversity and recreation.
This example shows that NBL is not “decoration”, but a guiding premise for location and design – with benefits for both operations, risk and site quality.
What can be transferred to holiday home fields?
Direct roof and surface water in an open chain (rainbed → vegetated ditches → sunken greenway), reduce pipes/culverts.
Use edge zones and vegetation for infiltration and erosion control.
Plan common green/blue structures early, not as "landscape additions."
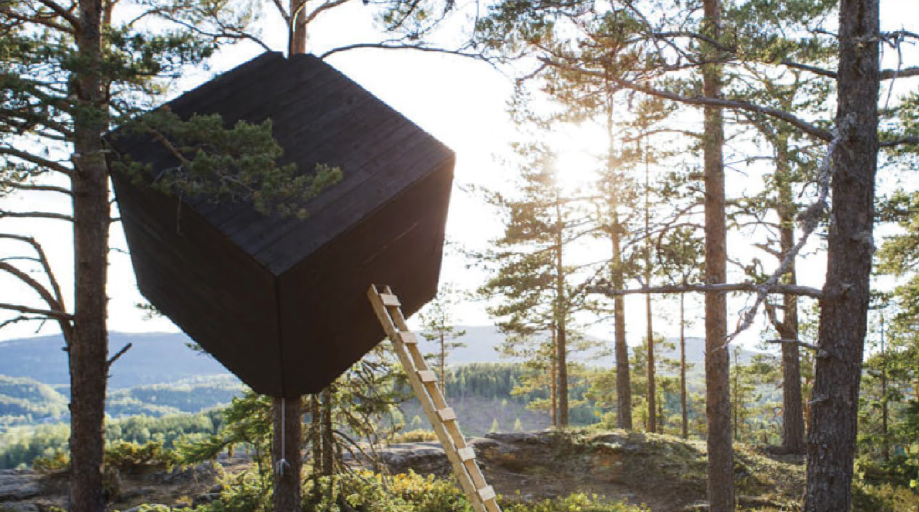
The Tree Cube, Höga kusten – "easy on the ground"
What does the case show?
Minimal footprint, terrain adaptation and nature integration: construction that follows the site and preserves vegetation/soil.
Exemplifies the basic idea in NBL for buildings: avoid and limit interventions before "adding" natural measures - reversibility, small volumes, point/screw foundations.
What can be transferred to holiday home fields?
Choose a location/method that minimizes mass displacement (build in micro terrain).
Use point foundations rather than poured slabs; preserve edge vegetation and trees.
Think "small, low, portable" as standard — nature tolerates it better, operation becomes easier.
Professional environment that has contributed to shedding light on the topic
White Architects
Contact info..
Nuclear power
Contact info..
Questions that are recommended to be discussed initially
What natural challenges are we dealing with (stormwater, erosion, heat, biodiversity)?
What ecosystem services already exist on/near the site – and how can we enhance them?
At what scale do we need to think for the measures to work (plot, sub-area, field, landscape)?
What is the project's level of ambition (avoid–limit–restore/enhance)?
What risks (floods, landslides, marshes, wetlands, vulnerable species) must guide choices and deselections?
How must the construction phase be adapted (season, access, soil compaction, establishment care)?
Proposal for role distribution
Business (developer/contractor): Propose level of ambition, identify benefits/costs, describe early NBL opportunities and opt-outs; plan for construction phase and maintenance.
Municipality/administration: Clarify relevant goals/requirements/consideration zones; point out risk factors; ensure that NBL is assessed from the start; clarify expectations for documentation.
Professional resources (consultants/architect/landscape architect) : Translate ambitions into feasible measures; contribute with map basis and principle sketches.